| 1 |
Product Description |
| 1.1 |
Product Vision |
| |
There are a large number of companies which are
importing and exporting goods in Singapore. However, there isn’t enough
space for storing the goods. |
| |
Belldoks Corporation decided to build a warehouse
a stretch of its land in Singapore. The warehouse will be opened to
other companies to store their goods at a reasonable rate. |
| |
To manage the warehouse efficiently, Belldoks
Corporation need a warehouse management system. So, the management of
Belldoks Corporation requested a software development company to develop
a WMS. |
| 1.2 |
Business Requirements |
| |
The first version of Belldoks Warehouse
Management System must be available within half of a year. |
| |
The system must increase the labor
productivity in 15% at least. |
| |
The system must result in 5% increasing
in shipping accuracy. |
| 1.3 |
Stakeholders and Users |
| |
Management – The director of software
development company to control the cost and charge. |
| |
Developers – The six-member development
team, which includes four software engineers and two experts in logistics. |
| |
Purchaser – Belldoks Warehouse Company
who invest money on the development. |
| |
Users – Warehouse operators, financial
staff and administration staff. |
| 1.4 |
Project Scope |
| |
The project will create software which
will help the warehouse to streamline the day to day activities. |
| 1.5 |
Assumptions |
| |
The incoming shipment will have customer
ID embedded in RFID tags. |
| |
The discount rates and deposit plans
will be decided offline. |
| |
The warehouse will do financial
transaction through cheque or bank transfer. |
| 1.6 |
Constraints |
| |
The system should support various types
of RFID scanner. |
| 2 |
Functional Requirements |
| 2.1 |
Startup |
| 2.1.1 |
When the webpage is loaded, the Warehouse Management Software should
load and execute. |
| 2.1.2 |
After the software is properly configured, the system should be able
to start reading in all the incoming and outgoing products that are
scanned. |
| 2.2 |
Product Scanner (RFID based) |
| 2.2.1 |
When the products come in, an identification tag should be pasted on
the package. |
| 2.2.1.1 |
The identification tag should contain the name of the product,
customer id, time, date of arrival, the location that it is going to be
stored as well as the barcode label. |
| 2.2.2 |
The staff would use the product scanner to scan all the incoming and
outgoing products to the warehouse. |
| 2.3 |
Database |
| 2.3.1 |
The database should store the details that were scanned in by the
product scanner. |
| 2.3.1.1 |
Details should include the product name, time and date of arrival of
shipment, the customer id associated with the package, location that the
package is stored. |
| 2.3.2 |
The software should be able to update necessary details in case of a
change |
| 2.3.2.1 |
Necessary details would include the customer information of the
product such as contact details. |
| 2.3.3 |
The database should allow the staff to manually input, change or
delete erase any details into the database in case of any error. |
| 2.3.4 |
The software should follow a standardised 24 hour clock format. |
| 2.3.5 |
The software should allow the staff to access the database 7 days a
week. |
| 2.4 |
Generation of Reports |
| 2.4.1 |
The system should be able to produce a monthly report of the current
inventory in the warehouse. |
| 2.4.1.1 |
Current inventory should include a list of all the products that are
currently stored in the warehouse and the respective IDs of customers
who have stored those products at that point of time . |
| 2.4.2 |
The system should be able to produce a report on the amount of
available space there is in the warehouse at that particular moment.
|
| 2.4.2.1 |
If the warehouse storage is already fully occupied, it should issue
a warning that the warehouse storage is already and that it would not be
able to accept any more orders from potential customers at that instant.
|
| 2.4.3 |
The system should be able to produce a yearly report on all the
details of previous or current customers. |
| 2.4.3.1 |
Details of customers should include Name of the person to be liaised
with, contact number, email id, current inventory of what that customer
has stored in the warehouse storage and previous transactions. |
| 2.4.4 |
The system should be able to produce a report based on tabulating
the cost of storing in the warehouse for each customer. |
| 2.5 |
Billing |
| 2.5.1 |
The software should be able to generate a receipt to bill the
customer at the point of billing. |
| 2.5.2 |
The software should allow the customer to choose the mode of
payment. |
| 2.5.2.1 |
The customer can choose between issuing a bank cheque or bank fund
transfer to the warehouse billing department. |
| 2.5.3 |
The software should be able to allocate the payment period for
customers depending on their contract. |
| 2.5.3.1 |
If the customer has a contract with the warehouse for a few years,
then the customer should be billed yearly. |
| 2.5.3.2 |
If the customer has a contract with the warehouse for a few months,
then the customer should be billed monthly. |
| 2.5.3.3 |
If the customer has a contract with the warehouse for less than a
month, then the customer should be billed when the contract expires.
|
| 2.6 |
Failures |
| 2.6.1 |
If the scanner is not able to read in the details of the barcode
label, it should issue a warning to the user. |
| 2.6.1.1 |
The user can then manually enter the details into the system. |
| 3 |
Data Requirements |
| 3.1 |
Warehouse data |
| 3.1.1 |
Each warehouse is identified by its alphanumeric ID. |
| 3.1.2 |
The alphabetical part of warehouse ID is mandatory and exactly one
alphabet long. |
| 3.1.3 |
The numeric part of warehouse ID is mandatory and ranges from
1-1000. |
| 3.1.4 |
Each warehouse is divided into two areas:
| i |
Free storage area |
| ii |
Rack storage area |
|
| 3.1.4.1 |
Free storage area is for packages that are too big to store in the
racks. |
| 3.1.4.2 |
Rack area is composed of storage racks. |
| 3.1.4.2.1 |
Racks are identified by racks numbers. |
| 3.1.4.2.2 |
Rack numbers are integers and unique within the warehouse. |
| 3.1.4.2.3 |
Racks are further subdivided into vertical sections. |
| 3.1.4.2.4 |
A warehouse may have a maximum of 1,000,000 racks |
| 3.1.4.2.5 |
A rack may have a maximum of 50 sections. |
| 3.2 |
Staff Data |
| 3.2.1 |
The system records the following information for each
employee:
| i |
Employee Name |
| ii |
Identification Number |
| iii |
Job Role |
| iv |
Working Hours |
|
| 3.2.2 |
Employee Name is a string of maximum length 30 characters. |
| 3.2.3.1 |
Employee ID is an alphanumeric string that starts with an alphabet
and ends with an alphabet. |
| 3.2.3.2 |
Employee ID can be maximum eight characters long and minimum two
characters long. |
| 3.2.4.1 |
Employee job role is the position/job that the employee carries out
at the company. |
| 3.2.4.2 |
Employee Job Role is stored as a string containing 0 to 20
alphanumeric characters. |
| 3.2.5.1 |
The employee working hours are stored in 24 hour format in local
time. |
| 3.2.5.2 |
The working hours are stored as four integers that denote:
| i |
starting hour |
| ii |
starting minute |
| iii |
ending hour |
| iv |
ending minute |
|
| 3.3 |
Customer Data |
| 3.3.1 |
The following information about each customer is stored:
| i |
customer id |
| ii |
name |
| iii |
customer address |
| iv |
customer phone |
|
| |
Customers are identified through their unique customer ID. |
| |
Customer ID is stored as an alphanumeric string, 1 to 16 characters
long. |
| |
Customer name is a string of alphabets and is maximum 30 characters
long. |
| |
Customer address is composed of Block, Street Name and ZIP code. |
| |
Customer address Block is an integer with maximum value 1000. |
| |
Customer Street Name is a string of 1 to 20 alphabets. |
| |
Customer ZIP code is 8 digit long. |
| 3.4 |
Shipment Data |
| 3.4.1 |
The warehouse receives commodities in shipments
which consist of packages of
the same commodity. |
| 3.4.2 |
The following information about each shipment
is recorded:
| i |
shipment id |
| ii |
customer id |
| iii |
vehicle id |
| iv |
number of packages |
| v |
date and time of check-in |
| vi |
date + time of checkout |
| vii |
staff in charge of the shipment |
| viii |
company delivering the package. e.g.
DHL/FedEx/COSCO/MAERSK/etc |
| ix |
company's reference |
|
| 3.4.3 |
Shipment ID is a alphanumeric key generated by
the system for tracking each shipment. |
| 3.4.3.1 |
Shipment ID is exactly 1 to 16 characters long. |
| 3.4.4 |
Customer ID is a alphanumeric key used identify
each customer. |
| 3.4.4.1 |
Customer ID is 1 to 16 characters long. |
| 3.4.5 |
Vehicle ID is the number on the identification
plate of the transport vehicle used to deliver the package to the
warehouse. |
| 3.4.5.1 |
Vehicle ID is 1 to 20 characters long. Allowed
characters are alphabets, numbers, colon(:) and hyphen(-). |
| 3.4.6 |
The number of packages in a shipment is an
integer with maximum value of 100,000. |
| 3.4.7 |
The date and time of checkin and checkout is
recorded in 24 hour format HHMM, in local time. |
| 3.4.8 |
The operator in charge of the shipment is
recorded via his/her staff/employee ID. |
| 3.4.9 |
The company delivering the package is stored as
a string of alphanumeric characters, with a maximum length of 20
characters. |
| 3.4.10 |
The company delivering the package can
optionally provide a shipping reference for tracking the shipment on
their side. |
| 3.4.10.1 |
The Customer Company's reference is stored as a
10 character alphanumeric string. Allowed characters are
alphabets, numbers and hyphen. |
| 3.5 |
Reservation Data |
| 3.5.1 |
A reservation contract is made when the customer reserves a space in
the warehouse. |
| 3.5.2 |
The following information related to a reservation contract is
stored in the system.
| i |
contract id |
| ii |
shipment id |
| iii |
customer id |
| iv |
amount charged |
| v |
free storage reserved |
| vi |
rack storage reserved |
| vii |
duration of reserve |
| viii |
deposit amount (default value 3 months) |
| ix |
discount rate |
|
| 3.5.3 |
The amount charged is a number with a maximum value of 1,000,000. |
| 3.5.4 |
Free storage reserved consists of a warehouse ID and free storage
floor area. |
| 3.5.5 |
Rack storage reserved consists of, possibly multiple sets of,
warehouse ID, rack number and section(s). |
| 3.5.6 |
The duration of reserve consists of a start date/time and end
date/time. Time is stored in 24 hour format in local time. |
| 3.6 |
Rates Data |
| 3.6.1 |
The following rental related parameters are stored by the system.
| i |
rental rates |
| ii |
handling charges |
|
| 3.6.2 |
Handling charge is the cost charged to the customer for the labour
associated with handling the package. |
| 3.6.3 |
These charges are flexible and are set by the warehouse
administrator. |
| 3.7 |
Billing Data |
| |
Bills in the WMS are represented by billing requests. Each billing
request has the following data:
| i |
shipment id |
| ii |
customer id |
| iii |
bill amount |
|
| |
Billing requests are created based on order parameters such as
reservation term and billing interval. Billing requests are created when
the reservation order is created. |
| |
Bill amount is an integer with a maximum value of 1,000,000. |
| 4 |
Non Functional Requirements |
| 4.1 |
Performance Requirements |
| 4.1.1 |
Time bounds |
| 4.1.1.1 |
The system should handle a minimum of 100 transactions per second. |
| 4.1.2 |
Reliability |
| 4.1.2.1 |
The system must have less than 1 hour downtime per 2 months . |
| 4.1.2.2 |
The system must be available for service when requested by users
(99%). |
|
4.1.2.3 |
The system must require no more than 1 hour per month of
maintenance. |
| 4.1.3 |
Security and Safety |
| 4.1.3.1 |
The system must ensure that the data is protected from unauthorized
access. |
| 4.1.3.2 |
All the system data must be backed up every 24 hours and the backup
copies should be stored in a secure location. |
| 4.1.3.2 |
The access permissions for system data may only be changed by the
system’s data administrator. |
| 4.2 |
Interface Requirements |
| 4.2.1 |
The system must be user-friendly (display informative error
messages). |
| 4.2.2 |
The system should be designed in such a way that it ensures loose
coupling. |
| 4.2.3 |
The system should promote reusability of code. |
| 4.3 |
Installation |
| 4.3.1 |
The system must be installable on the webserver in no more than 1
hour. |
| 4.4 |
General Operation |
| 4.4.1 |
A configuration file must be prepared at installation so that the
Warehouse Management System (WMS) can read this file to obtain its
configuration at startup. |
| 4.5 |
Hardware |
| 4.5.1 |
The system should be able to run on a running Linux with 100M of
available disk space. |
| 4.6 |
Resource Requirements |
| 4.6.1 |
The system must use as little CPU, memory usage as possible. |
| 4.7 |
Failure |
| 4.7.1 |
The system must fail no more than once per month of normal
operation. |
| 4.7.2 |
The system must recover from power failures. |
| 4.7.3 |
Scanner failures must be detectable when a scanner reads. |
| 5 |
Interface Requirements[external link] |
| 6 |
Use Case Models |
| 6.0 |
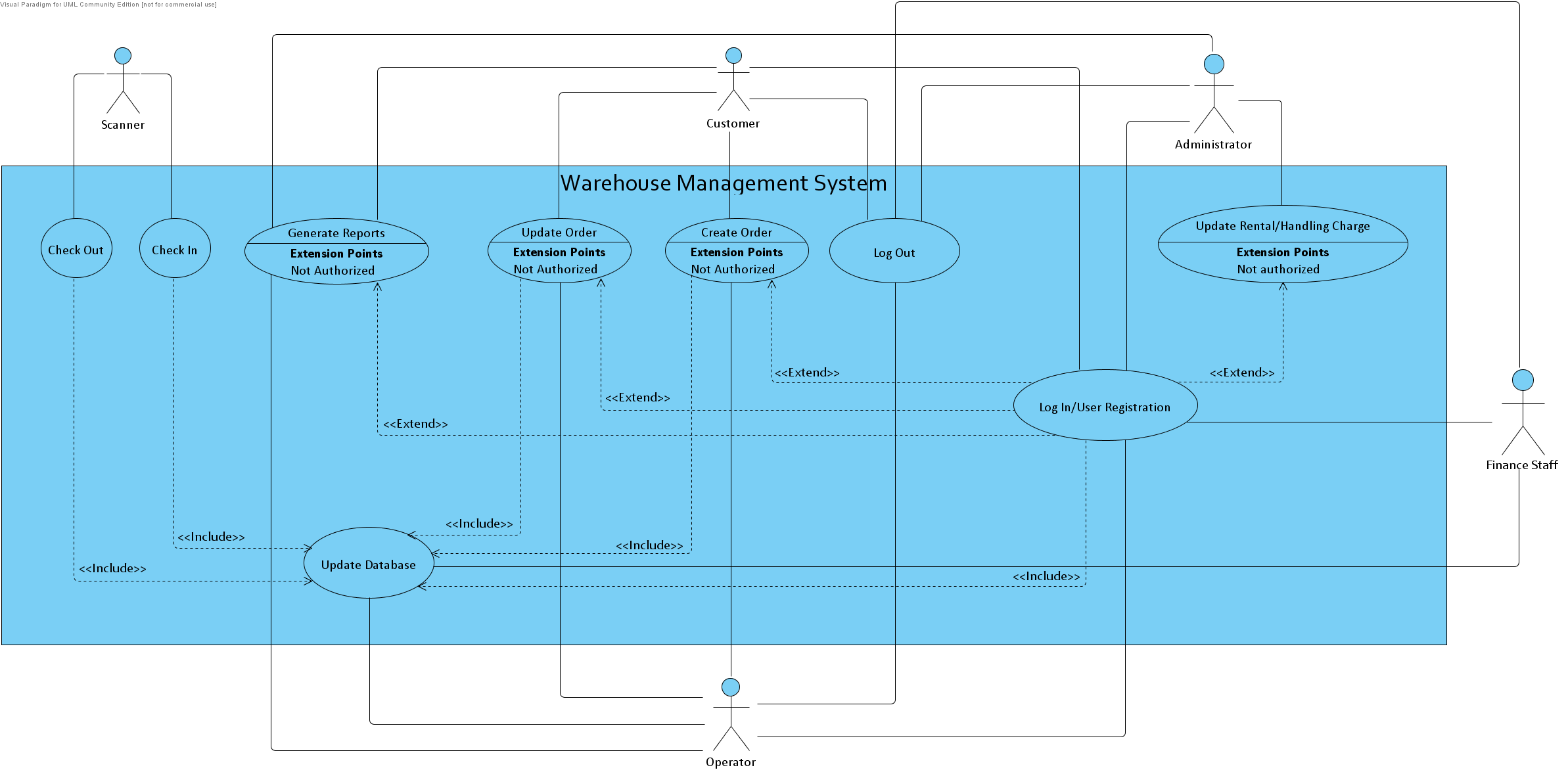
|
| 6.1 |
| Use Case ID |
1 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Update rental and handling charges |
|
|
| Created By |
Bai Lu |
Last Updated By |
Bai Lu |
| Date Created |
23 Jan, 2009 |
Date Last Updated |
30 Jan,2009 |
| Actors |
Administrator |
| Description |
Administrator update the charge rate for basic unit of
spaces and handling |
| Trigger |
Administrator logs on the system, and starts to update. |
| Preconditions |
| Administrator is authorized. |
| It’s necessary to change the charge rate. |
|
| Postconditions |
| The data in the bill would be updated. |
| Those charges before updating the rate remains the same
based on the contracts. |
|
| Normal Flow |
| 1 | Administrator log on the system |
| 2 | Administrator input the username, password and domain
into computer. |
| 3 | Website check the database for the authorization of the
username. |
| 4 | Based on the order from management, administrator
input new charge rate information. |
| 5 | Save data. |
| 6 | Database gets updated. |
|
| Alternative Flows |
N.A. |
| Exceptions |
| 1.0.E.1 |
Website failed to authorize the user’s identity. |
| |
| 1.0.E.1.1 |
User’s input is wrong: Error message:
Retype. |
| 1.0.E.1.2 |
Database error: Use case ends |
|
| 1.0.E.2 |
The information cannot be saved. |
| |
| 1.0.E.2.1 |
Database design mistake: Use case ends. |
|
| 1.0.E.3 |
Administrator does not confirm the updates: Use case
ends. |
| 1.0.E.4 |
Administrator cancel the output phase: Use case ends. |
|
| Includes |
N.A. |
| Priority |
N.A. |
| Frequency of Use |
Approximately 2 times/month |
| Business Rules |
N.A. |
| Special Requirements |
N.A. |
| Assumptions |
| 1 |
The charge rate needs to be updated from time to
time. |
| 2 |
When calculating the bill automatically, system
fetch charge rate from database. |
| 3 |
Old contracts would not change after updating the
charge rate. |
|
| Notes and Issues |
N.A. |
|
| 6.2 |
| Use Case ID |
2 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Register User and Log In |
|
|
| Created By |
Deepika Sridhar |
Last Updated By |
Deepika Sridhar |
| Date Created |
8th Feb 2009 |
Date Last Updated |
8th Feb 1009 |
| Actors |
Operator, Administrator, Customer |
| Description |
This use case is used in the following situations:
| 1 |
When the user is a first time user and does not have
a username or password to sign into the system. |
| 2 |
When the user wants to access the database which
contains all the details such as the inventory list at
each storage location, the shipment details of each
package, the customer details and more. If the user is a
first time user, he would need to register for an
account. |
|
| Trigger |
When the user attempts to access any area/function that
requires authorization |
| Preconditions |
The user wants to access the database to view, modify or
update some information in the database |
| Postconditions |
The user is in the system accessing the database. |
| Normal Flow |
| 2.1 |
When the system displays the login screen |
| 2.2 |
The user has to input his username and password into the login screen |
| 2.3 |
The user then has to click on the login button |
| 2.4 |
The user has to wait for the system to access its own database to check
whether the username and password is valid
|
| 2.5 |
If the username and password is valid, mark the user as
authorized user
|
| 2.6 |
Display the homepage of the warehouse management |
|
| Alternative Flows |
When the user is a first time user:
| 2.1.1 |
User will have to click on signup button |
| 2.1.2 |
User will be directed to a registration page where
they have to fill up an application with their
particulars |
| 2.1.3 |
The user has to choose a unique username and
password |
| 2.1.4 |
User will have to click submit |
| 2.1.5 |
The system would check the database whether the
username is unique |
| 2.1.6 |
The system would store the username and its password
in the database |
| 2.1.7 |
The user will be directed to the to the login screen |
| 2.1.8 |
The user has to input his new username and password
into the login screen |
| 2.1.9 |
The user then has to click on the login button |
| 2.1.10 |
The user has to wait for the system to access its
own database to check whether the username and password
is valid |
| 2.1.11 |
If the username and password is valid, mark the user
as authorized user |
| 2.1.12 |
Display the homepage of the warehouse management |
|
| Exceptions |
| 2.0.E.1 |
The user failed to authenticate the username and
password.
| 2.0.E.1.1 |
User can try up to a maximum of 3 times |
| 2.0.E.1.2 |
If the problem still continues, they can
contact the administrator at the warehouse for
help. |
|
| 2.1.E.1 |
The username that the new user is entering in the
registration module is not unique .
| 2.1.E.1.1 |
User has to keep thinking of an alternative
unique username until he is able to find one.
|
|
|
| Includes |
N.A. |
| Priority |
N.A. |
| Frequency of Use |
Whenever a user wants to access the system. It is used very
frequently. |
| Business Rules |
N.A. |
| Special Requirements |
N.A. |
| Assumptions |
Each kind of user is only allowed to access certain part of
the database. |
| Notes and Issues |
N.A. |
|
| 6.3 |
| Use Case ID |
3 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Log Out |
|
|
| Created By |
Bai Lu |
Last Updated By |
Bai Lu |
| Date Created |
8 Jan, 2009 |
Date Last Updated |
8 Jan,2009 |
| Actors |
Operator, Administrator, Customer |
| Description |
This use case is used when the user finish the work and want
to leave the system. |
| Trigger |
When the user click the log out button |
| Preconditions |
The user finishes the access to database to view, update and
delete, and wants to leave the system. |
| Postconditions |
The user is authorization is of the system invalidated. |
| Normal Flow |
| 3.1 |
User click the log out button |
| 3.2 |
system ask if the user really wants to leave, user
chooses yes |
| 3.3 |
system ask if the user wants to leave with saving
data or not, user chooses either one. user is out of
the system |
|
| Alternative Flows |
N.A. |
| Exceptions |
| 3.0.E.1 |
System error displayed
| 3.0.E.1.1 |
System automatically logs out the user after
10 seconds |
|
| 3.0.E.2 |
user closes the browser directly
| 3.0.E.2.1 |
System automatically logs out the user after
10 seconds |
|
| 3.0.E.3 |
User chooses no: user goes back to the system again
and use case ends |
|
| Includes |
N.A. |
| Priority |
N.A. |
| Frequency of Use |
It is used very frequently. Depends on the customer number. |
| Business Rules |
N.A. |
| Special Requirements |
N.A. |
| Assumptions |
N.A. |
| Notes and Issues |
N.A. |
|
| 6.4 |
| Use Case ID |
4 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Generate Reports |
|
|
| Created By |
Kavitha D/O Ginanam |
Last Updated By |
Bai Lu |
| Date Created |
1 Feb, 2009 |
Date Last Updated |
5 Feb, 2009 |
| Actors |
Warehouse Operator, Customer, Administrator |
| Description |
This use case deals with the generation of reports. This use
case is invoked in the following conditions:
| 1 |
Reports on available space need to be generated. |
| 2 |
Reports on previous/current customers need to be
generated. |
| 3 |
Reports on the inventory need to be generated. |
| 4 |
Reports on tabulation of rental space need to be
generated. |
|
| Trigger |
The user requests for the generation of the various reports. |
| Preconditions |
The user’s identity is authorized. |
| Postconditions |
Display reports |
| Normal Flow |
| 4.1 |
The user requests for the generation of reports
screen. |
| 4.2 |
WMS (Warehouse Management System) displays the
choice of reports that a user wants to generate. |
| 4.3 |
The user selects the report he/she wants to
generate. |
| 4.4 |
The different kinds of reports will be generated in
html. |
|
| Alternative Flows |
| 4.1 |
The customer requests for the generation of
reports. |
| 4.2 |
The inventory reports will be generated in html. |
|
| Exceptions |
| 4.0.E.1 |
The generation of reports fails. Error message
like “Generation of this report fails” would be
displayed. |
| 4.0.E.2 |
The user tries to generate a report without
authentication. And due to this, the user would be
redirected to the login screen. |
| 4.0.E3 |
The WMS is forced to terminate during the process.
In this case, no generation of reports would occur. |
|
| Includes |
N.A. |
| Priority |
N.A. |
| Frequency of Use |
very frequently. |
| Business Rules |
N.A. |
| Special Requirements |
N.A. |
| Assumptions |
N.A. |
| Notes and Issues |
N.A. |
|
| 6.5 |
| Use Case ID |
5 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Check In |
|
|
| Created By |
Ezra Yap |
Last Updated By |
Subrat Meher |
| Date Created |
04 Feb,2009 |
Date Last Updated |
09 Feb,2009 |
| Actors |
Operator, Scanner |
| Description |
To permit the Operator and Scanner to scan and identify all
incoming stock or good. The recording process is made after all
the incoming good are identified and the date of arrival of good
is in order. |
| Trigger |
Operator identifies the incoming stock that comes with the
ID number and record in the details. Scanner will automatically
scan the incoming good that comes with barcode label. |
| Preconditions |
Scanner machine is started and logged in the WMS and is
ready to scan. |
| Postconditions |
All incoming goods are recorded in the WMS. |
| Normal Flow |
| 5.1 |
When a shipment arrives, the scanner scans the good
and the WMS matches the ID received from the scanner to
a order reservation. |
| 5.2 |
The incoming good is recorded in the WMS. |
| 5.3 |
When the operator logs in to the WMS, he verifies
the incoming shipment and the operator is recorded
together with the shipment as the operator handling the
shipment and the check in is completed. |
|
| Alternative Flows |
N.A. |
| Exceptions |
| 5.0.E.1 |
WMS fails to identify the tag on the incoming
shipment.
| 5.0.E.1.1 |
Manually enter the shipment ID on the
shipment. |
|
| 5.0.E.2 |
Scanner is not ready or not working properly.
| 5.0.E.2.1 |
Manually enter the shipment ID. |
|
| 5.0.E.3 |
The shipment ID already exists and has been checked
in.
| 5.0.E.3.1 |
Physically intervene and verify that the
good is in place. If good already exists, create
a new temporary shipment ID subject to
verification with customer company. |
|
|
| Includes |
N.A. |
| Priority |
N.A. |
| Frequency of Use |
Directly proportional to the number of goods checking in.
Approximately 1 every 10 minutes or 150 per day. |
| Business Rules |
N.A. |
| Special Requirements |
N.A. |
| Assumptions |
N.A. |
| Notes and Issues |
N.A. |
|
| 6.6 |
| Use Case ID |
6 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Check Out |
|
|
| Created By |
Lee Joon Kiat |
Last Updated By |
Lee Joon Kiat |
| Date Created |
1 Feb, 2009 |
Date Last Updated |
6 Feb, 2009 |
| Actors |
Scanner, Operator |
| Description |
Operator uses scanner to scan the products. The detail of
the products is checked through the system and marked as
checked-out. |
| Trigger |
Customer requests for checking out their products. |
| Preconditions |
The contract that the customer made with the warehouse
company expires. |
| Postconditions |
Record of check out is inputted into the system. The
particular products are marked as checked out to the customer. |
| Normal Flow |
| 6.1 |
Customer requests for checking out their products
through the system. |
| 6.2 |
Operator uses the system to check the location and
quantity of the particular products. |
| 6.3 |
Operator inputs the checkout records into the
system. |
| 6.4 |
Scanner is used to scan the products. |
| 6.5 |
The products are marked as checked-out. |
|
| Alternative Flows |
N.A. |
| Exceptions |
| 6.0.E.1 |
The product cannot be
found physically.
| 6.0.E.1.1 |
The system sends a message to the
admin staff. |
|
|
| Includes |
N.A. |
| Priority |
N.A. |
| Frequency of Use |
N.A. |
| Business Rules |
N.A. |
| Special Requirements |
N.A. |
| Assumptions |
The scanner is working well with the system. |
| Notes and Issues |
N.A. |
|
| 6.7 |
| Use Case ID |
7 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Update database |
|
|
| Created By |
Lee Joon Kiat |
Last Updated By |
Lee Joon Kiat |
| Date Created |
7 Feb, 2009 |
Date Last Updated |
8 Feb,2009 |
| Actors |
Administrator, Operator |
| Description |
Update the database while other operations are performed,
like check in, check out, create order, update order, etc.. |
| Trigger |
Operations requiring database updates are performed. |
| Preconditions |
The data in database is maintained well |
| Postconditions |
The database is updated with new and correct information. |
| Normal Flow |
| 7.1 |
Other operations requiring database update are
performed. |
| 7.2 |
Data is inserted or updated. |
| 7.3 |
The database contains updated and correct data. |
|
| Alternative Flows |
| 7.1 |
Administrator and operator update the database
manually. |
|
| Exceptions |
| 7.0.E.1 |
The inserted data is incorrect.
| 7.0.E.1.1 |
The database rejects the insertion. |
|
|
| Includes |
N.A. |
| Priority |
N.A. |
| Frequency of Use |
Base on the rate of order creation, check in, check out, etc |
| Business Rules |
N.A. |
| Special Requirements |
N.A. |
| Assumptions |
The database is maintained by a database management system. |
| Notes and Issues |
N.A. |
|
| 6.8 |
| Use Case ID |
8 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Update Order Details |
|
|
| Created By |
Subrat Meher |
Last Updated By |
Subrat Meher |
| Date Created |
7 Feb, 2009 |
Date Last Updated |
7 Feb, 2009 |
| Actors |
Customer, Operator |
| Description |
This use case deals with the creation and modification of
reservation orders. This use case is invoked when:
| 1 |
order/reservation information is wrongly input |
| 2 |
the customer wishes for an early check out of his
goods. |
|
| Trigger |
User initiates an update order request |
| Preconditions |
| 1 |
The user is authenticated and logged in. |
| 2 |
The user has located the order to be updated. |
|
| Postconditions |
The information of an existing reservation order will be
updated , and a change notification will be dispatched to the
operator console. |
| Normal Flow |
| 8.1 |
The user requests to update an existing order. |
| 8.2 |
The user updates the desired checkout time. |
| 8.3 |
An order update notification is sent to the operator
console. |
|
| Alternative Flows |
N.A. |
| Exceptions |
| 8.0.E.1 |
The WMS is forced to terminate during the process.
In this case, no modifications to the database should
occur and the database should be at the same state as it
was right before initiating the order process. |
| 8.0.E.2 |
The user tries to update an order without
authentication. In this case, the user should be
redirected to the login screen. |
|
| Includes |
Update Database |
| Priority |
Log-In |
| Frequency of Use |
Approximately Once every five reservation transactions |
| Business Rules |
N.A. |
| Special Requirements |
|
| Assumptions |
| 1 |
The user is only allowed to update the checkout time
of his goods. |
| 2 |
The reservation cannot be cancelled even if the
goods are checked out. |
|
| Notes and Issues |
|
|
| 6.9 |
| Use Case ID |
9 |
|
|
| Use Case Name |
Create New Order |
|
|
| Created By |
Subrat Meher |
Last Updated By |
Subrat Meher |
| Date Created |
3 Feb, 2009 |
Date Last Updated |
9 Feb, 2009 |
| Actors |
Customer, Operator |
| Description |
This use case deals with the creation and modification of
reservation orders. This use case is invoked when new warehouse
space needs to be reserved. |
| Trigger |
User requests creation of a new reservation order |
| Preconditions |
The user is authenticated and logged in. |
| Postconditions |
A new order will be created |
| Normal Flow |
| 9.1 |
User requests creation of new order. |
| 9.2 |
WMS displays the rack selection screen |
| 9.3 |
The user creates a custom plan. |
| 9.4 |
The rack spaces requested by the user are saved
temporarily (on client side?), to be confirmed upon
payment (and marked as being viewed). |
| 9.5 |
The WMS displays the lease term. |
| 9.6 |
The user selects the desired lease term. |
| 9.7 |
The WMS displays the payment screen. |
| 9.8 |
The user chooses the payment period and any other
required details for the payment method. |
| 9.9 |
The WMS records the payment details and generates
and stores all the bill requests. |
| 9.10 |
The order information is recorded and the rack
spaces are marked as reserved. |
| 9.11 |
Upon completion of any initial payment (if
required), the order is marked confirmed. |
| 9.12 |
Optionally, an email confirmation to the customer is
dispatched. |
|
| Alternative Flows |
| 9.3.1 |
A plan is automatically generated for the user. |
|
| Exceptions |
| 9.0.E.1 |
The WMS is forced to terminate during the process.
In this case, no modifications to the database should
occur and the database should be at the same state as it
was right before initiating the order process. |
| 9.0.E.2 |
The user tries to make an order without
authentication. In this case, the user should be
redirected to the login screen. |
| 9.0.E.3 |
There is no space in the warehouse. The user should
be alerted that there is no space in the warehouse and
the use case should be aborted without any changes to
the database. |
| 9.0.E.4 |
If there is no payment for the initial payment for
three days, a reminder email to the payer will be sent.
At six days, the reservation will be highlighted to the
billing department for action. |
| 9.1.E.1 |
If automatic plan generation fails for some reason,
the user is redirected to the custom plan creation
screen, together with an error message indicating the
plan generation failure. |
|
| Includes |
Update Database |
| Priority |
Login |
| Frequency of Use |
Approximately once every five reservation transactions |
| Business Rules |
Company’s information policy - Storing customer details. |
| Special Requirements |
N.A. |
| Assumptions |
| 1 |
Shipments carry RFID tags for linking shipment to
reservation order |
| 2 |
The warehouse accepts payments only via offline
payments through cheque. |
|
| Notes and Issues |
N.A. |
|
